Project Description: The Puuloa Rifle range berms are some of the tallest and largest rifle berms in the Pacific region and stand 22 feet high and 650 feet in length. HIES scope entailed design, de-leading, hazardous material testing (EA), and erosion/slope control implementation of Range A andB located in the Puuloa Training facility at Ewa Beach, HI. HIES designed and subsequently implemented an erosion control plan using civil, structural, GIS, and Geophysical engineers for berms A and B to control soil, slope, and water erosion on the berms. The erosion design was implemented due to the possibility that a 15’ tall 550’ long concrete bullet deflecting wall located on top of the earthern 22’ tall berm had the possibility of collapse due the undermining of the berm caused by natural erosion and bullet impact. The erosion control berm design used geogrids for benching and slope retention thus using no metals or materials that would cause bullet deflection. This was a unique solution and may be the first of its kind.
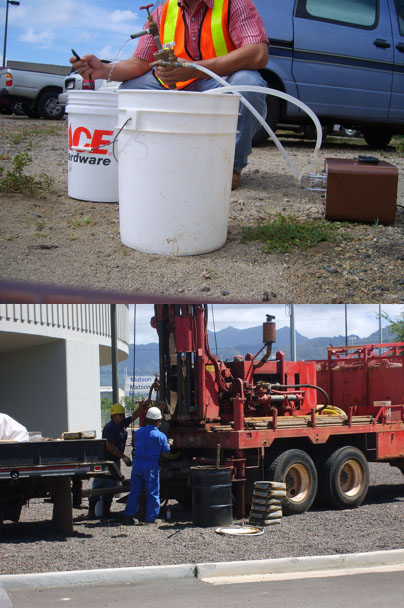
The de-leading process used a soil-washing method from a mobile equipment where HIES physically performed lead, UXO, and metals remediation. The rifle range uses M-9, M-16, and up to a 7.62 caliber where upon impact, most of the rounds would explode to fragmented pieces. To clean the fragmented lead and whole bullets including shells, penetrators, and shots, HIES utilizes a 4 screen, trommel, and soil washing system where soils and materials placed back on the berms would reduce future maintenance costs by 50%. This mobile system is cost effective due to its ease of transport and size thus enabling the company to minimize the range facilities closure time and exposure. If UXO / Live rounds are not detected during physical exams, the dirt is passed through a heavy steel compartment of screens where it will most likely be detected. This compartment protects labor personnel against discharge. This new method greatly reduces maintenance cost of traditional earthern berms and will also save the clients from investing in costly bullet trap alternatives.
Soil, water, compaction, and air monitoring testing was conducted at different phases of the project to test hazmat levels at all firing lines for future remediation projects. These tests were conducted to measure lead and contamination levels that may effect the health of shooters.